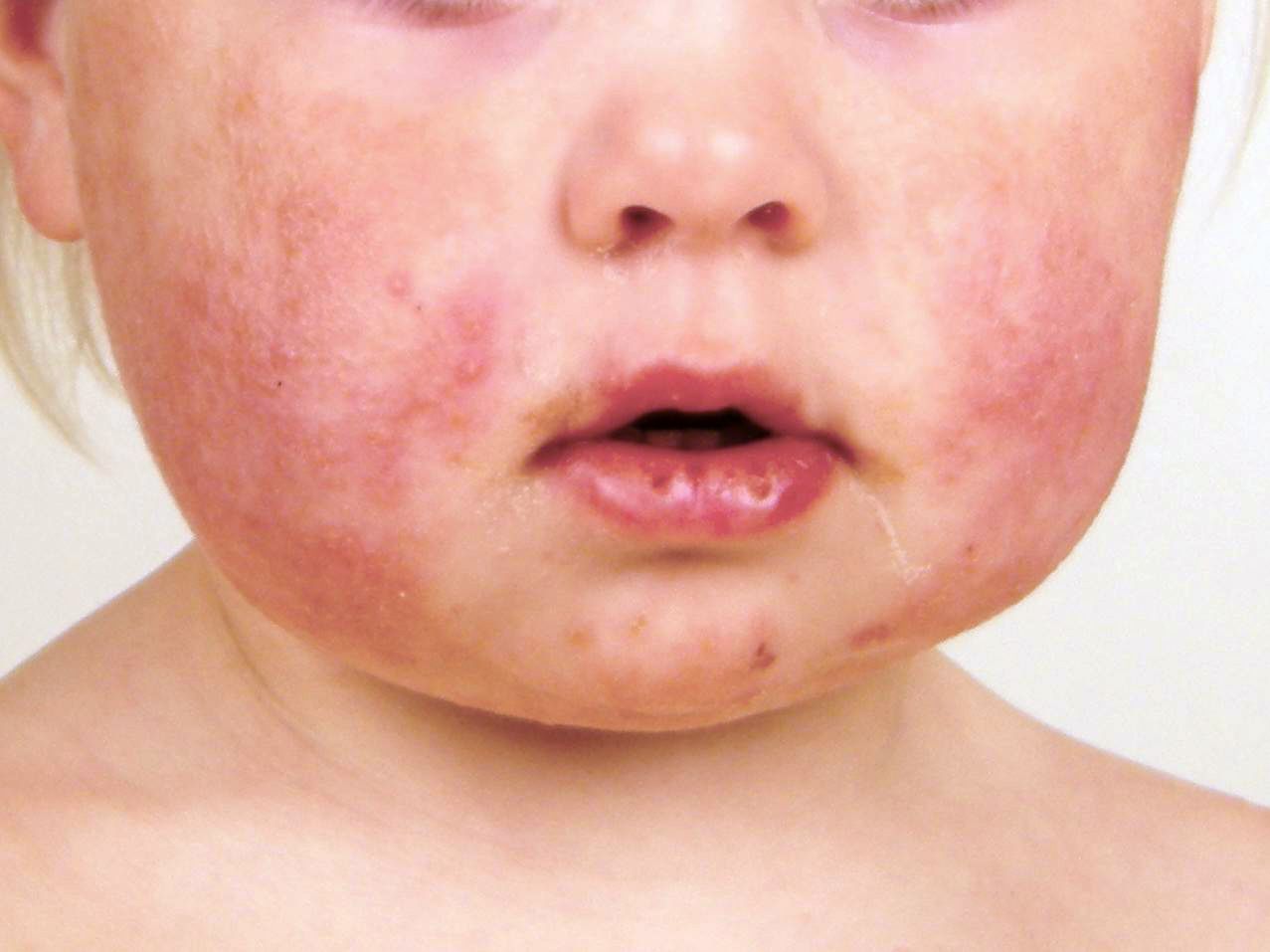
What is a disease and what causes the disease?
A disease is any abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of part or all of an organism, and that is not a direct result of physical injury. In humans, diseases often lead to symptoms such as pain, discomfort, organ dysfunction, or abnormal physical or mental states.Diseases can affect different parts of the body, and they may be short-term (acute) or long-term (chronic). Some diseases can be easily treated, while others may be life-threatening.
What Causes Diseases?
Diseases can be caused by a wide range of factors. These causes are generally divided into the following categories:
1. Infectious Causes
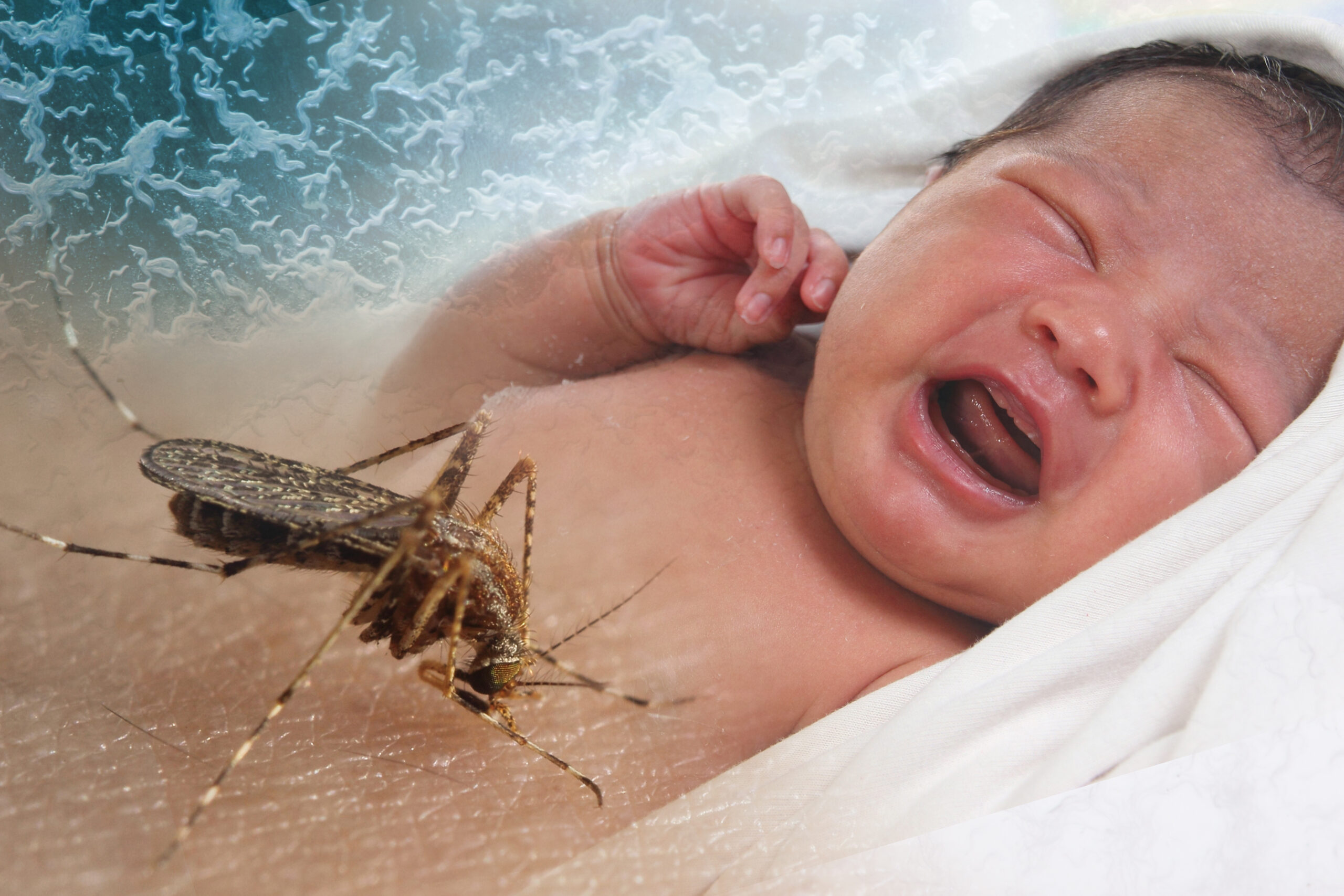
Diseases caused by microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites. These are known as infectious diseases and can spread from person to person, animals, or the environment.
Examples:
- Bacteria: Tuberculosis, Pneumonia
- Viruses: COVID-19, Influenza, HIV/AIDS
- Fungi: Ringworm, Candidiasis
- Parasites: Malaria, Worm infections
2. Genetic Causes
Some diseases are caused by abnormalities in the DNA, inherited from parents. These are known as genetic or hereditary diseases.
Examples:
- Down syndrome
- Sickle cell anemia
- Cystic fibrosis
3. Lifestyle and Behavioral Causes
Unhealthy lifestyle choices can increase the risk of developing certain diseases, especially chronic conditions.
Examples:
- Smoking → Lung cancer, Heart disease
- Poor diet → Obesity, Diabetes
- Lack of exercise → Cardiovascular disease
- Excessive alcohol consumption → Liver disease
4. Environmental Causes
Exposure to harmful environmental factors can also cause diseases.
Examples:
- Air pollution → Asthma, Respiratory problems
- Radiation exposure → Cancer
- Chemical exposure → Skin diseases, Poisoning
5. Nutritional Deficiencies
A lack of essential nutrients can lead to disease.
Examples:
- Vitamin C deficiency → Scurvy
- Iron deficiency → Anemia
- Iodine deficiency → Goiter
6. Autoimmune Causes
In some cases, the body’s immune system attacks its own cells and tissues, leading to autoimmune diseases.
Examples:
- Type 1 diabetes
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Lupus
7. Degenerative Causes
These diseases result from the gradual deterioration of body tissues and organs, often related to aging.
Examples:
- Osteoarthritis
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease